Point of Sale System: What is it and how it works?
Are you confused about whether to get started with the point-of-sale system or not? If yes, this article will clear all your doubts. Scroll till the last to know how point-of-sale system can be a game changer for your business.
What is the point of sale system?
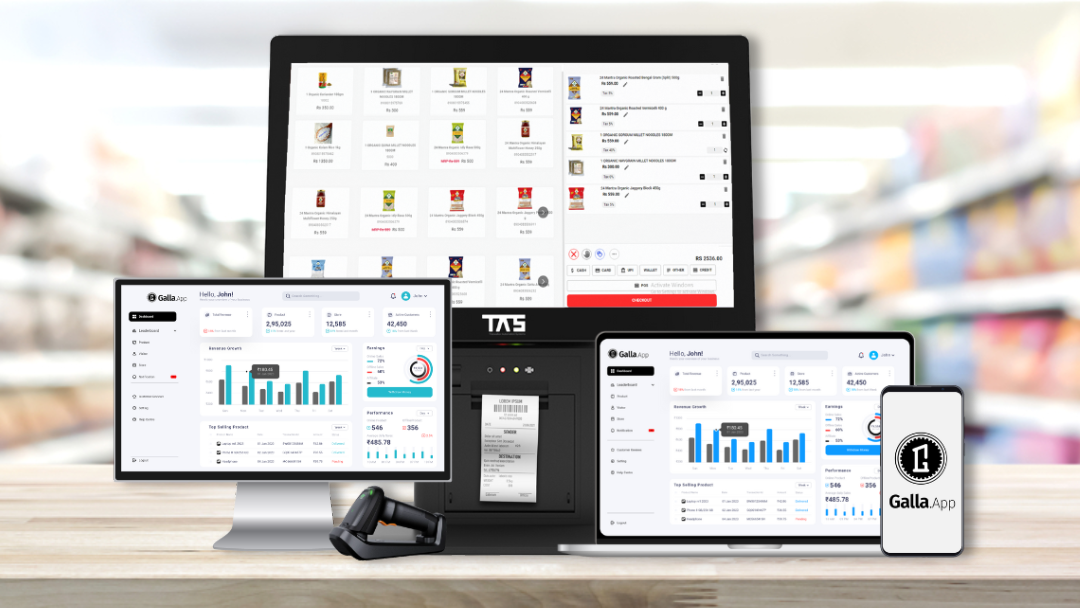
A point-of-sale system, also known as a POS system, is a computerized system businesses use to conduct sales transactions with customers. It typically includes hardware such as a cash register, barcode scanner, receipt printer, and credit card terminal, as well as software for processing payments, managing inventory, and generating sales reports.
The primary purpose of a point-of-sale system is to streamline and automate the sales process, making it easier for businesses to accept payments, track sales data, and manage their operations efficiently.
Key Functions:
1) Transaction Processing: Handles the payment process by calculating the total cost of the items purchased, applying taxes, and generating receipts.
2) Payment Methods: Accepts various forms of payment, including cash, credit/debit cards, and mobile payments.
3) Inventory Management: Tracks inventory levels, updates stock based on sales, and can reorder products when stock is low.
4) Sales Reporting: Provides detailed sales reports and analytics, helping businesses understand sales trends and make informed decisions.
5) Customer Management: Stores customer data, tracks purchase history, and supports loyalty programs and promotions.
Components:
1) Hardware:
- Terminal/Computer: The main device that runs the POS software.
- Monitor/Display: Shows transaction details and interfaces for the cashier.
- Barcode Scanner: Reads product barcodes for quick item entry.
- Card Reader: Processes credit/debit card payments.
- Receipt Printer: Prints transaction receipts for customers.
- Cash Drawer: Secures cash transactions.
-
-
2) Software:
- POS Software: The application that handles all transaction processes, inventory management, and sales reporting.
- Operating System: The underlying system software that runs the POS application.
-
How does a point-of-sale system work?
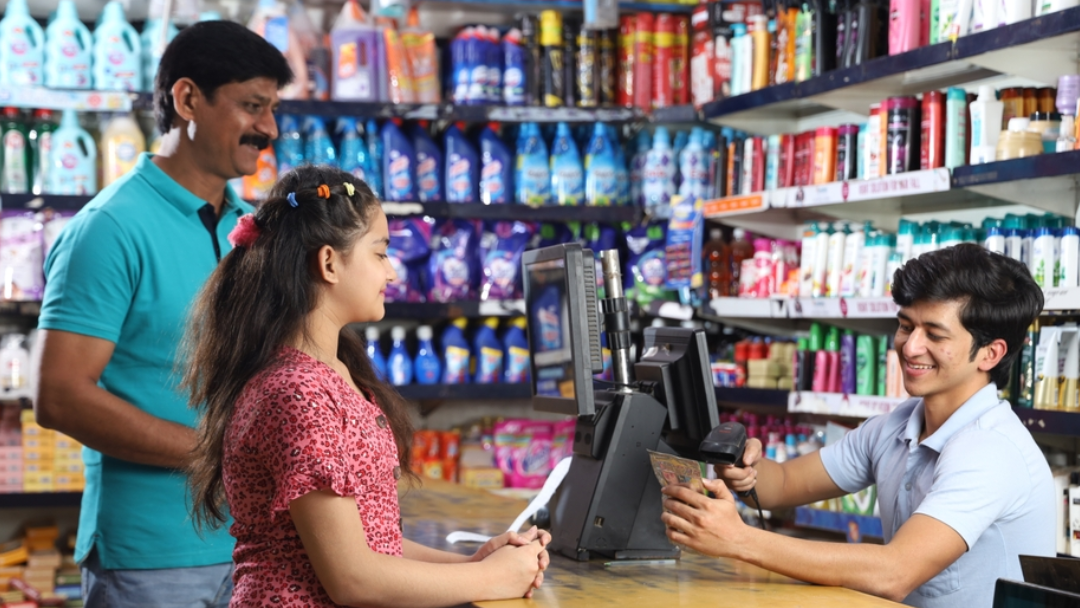

A Point of Sale (POS) system works through a combination of hardware and software to facilitate sales transactions and related processes. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how a POS system typically operates:
1) Item Entry:
- Barcode Scanning: The cashier scans the barcodes of the items being purchased using a barcode scanner. The POS system retrieves the product information from its database.
- Manual Entry: If an item doesn’t have a barcode, the cashier can manually enter the product code or select the item from a menu.
2) Price Calculation:
- Automatic Calculation: The POS software calculates the total price, including any applicable taxes and discounts.
- Promotions/Discounts: Any promotional discounts or loyalty rewards are applied automatically.
3) Payment Processing:
- Payment Method Selection: The customer selects a payment method (cash, credit/debit card, mobile payment, etc.).
- Card Processing: If paying by card, the customer inserts, swipes, or taps their card on the card reader. The POS terminal communicates with the payment processor to authorize the transaction.
- Authorization: The payment processor verifies the payment details, checks for available funds, and either approves or declines the transaction.
- Cash Handling: If paying by cash, the cashier inputs the amount received, and the system calculates any change due.
4) Receipt Generation:
- Digital or Printed Receipt: The POS system generates a receipt, which can be printed or sent digitally via email or SMS based on the customer’s preference.
5) Inventory Management:
- Stock Update: The POS system automatically updates the inventory levels, reducing the stock count for the sold items.
- Reorder Alerts: If stock levels fall below a certain threshold, the system can trigger alerts or automatic reorder processes.
6) Sales Reporting:
- Data Collection: The POS terminal collects data on each transaction, including item details, time of sale, payment method, and customer information if available.
- Analytics: This data is used to generate reports on sales performance, peak hours, popular products, and other metrics useful for business management.
7) Customer Management:
- Loyalty Programs: If integrated with a loyalty program, the POS terminal can update customer points, apply discounts, and manage rewards.
- Customer Profiles: The system can store customer information, purchase history, and preferences for personalized service and marketing.
8) Integration with Other Systems:
- Accounting: Sales data can be synchronized with accounting software to streamline financial reporting.
- E-commerce: POS systems can integrate with online stores, ensuring consistency in inventory and pricing across channels.
- CRM Systems: Customer data from the POS can be used in customer relationship management (CRM) systems for targeted marketing and improved customer service.
10) Security:
- Data Encryption: Payment data is encrypted to protect against fraud.
- User Authentication: Access to the POS system is usually controlled through user IDs and passwords or biometric authentication.
Workflow Example:
- Once the items are chosen, the customer brings them to the checkout.
- Cashier scans items or manually enters them.
- POS system calculates total cost and applies discounts/taxes.
- Customer chooses payment method and completes the transaction.
- POS updates inventory, generates receipt, and stores transaction data.
- Business owner accesses sales reports and analytics for decision-making.
By automating and streamlining these processes, POS system help businesses operate more efficiently, enhance customer service, and maintain accurate records.
Should businesses incorporate point-of-sale system?
Yes, Businesses should incorporate Point of Sale (POS) systems to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. POS systems streamline transactions, reduce errors, and offer real-time inventory management, helping prevent stock issues. They provide detailed sales reports, aiding data-driven decisions and integration with accounting and CRM systems. Secure payment processing ensures data protection, while multiple payment options and personalized service improve the customer experience. Although there is an initial investment and training required, the long-term benefits of increased productivity, better inventory control, and improved customer relations make POS systems a valuable addition for most businesses.
SUMMING UP
For most businesses, especially those in retail, hospitality, and service industries, incorporating a POS system can significantly enhance operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall profitability. The benefits of accurate data management, improved inventory control, and streamlined transactions therefore make POS systems crucial for modern businesses.

